Women are more likely to be diagnosed with cervical osteochondrosis than men. This is not only due to the lower strength of the ligament-tendon apparatus, the weakness of the muscular corset. Throughout her life, a woman's body is subject to fluctuations in hormone levels that can adversely affect the condition of cartilage and bone tissue. However, there is little difference between conservative and surgical treatment of cervical osteochondrosis in both sexes.
Features of osteochondrosis in women
The development and progression of cervical osteochondrosis in women is the same as in men. The disc loses its ability to retain water and begins to slowly collapse, involving bone structures, ligaments, and tendons in the process. But because of weaker neck muscles and weaker vertebrae, women's first symptoms appear more quickly. Already in the initial stages of development, there may be noticeable discomfort that restricts mobility.
It should be noted that women of any age have lower stress tolerance. After learning that a complete cure for osteochondrosis is impossible, they can put themselves into a state of depression through experience. Therefore, antidepressants, antipsychotics, sedatives, and tranquilizers are often included in treatment regimens.
Causes of the disease in women
The main reason women experience more frequent disc injuries is a decrease or increase in hormone levels in the body. After natural menopause begins, the production of estrogen, which is involved in regulating the biosynthesis of cartilage and bone tissue, gradually decreases. Decreased estrogen levels during menopause can cause disc damage, leading to osteoporosis (increased bone fragility).
Women monitor their weight, so they often reject calcium-rich foods—sour cream, cheese, peas, soybeans, beans. If the diet is followed, not only weight loss, but also deficiencies in the most important trace elements and vitamins, which can lead to premature destruction of the intervertebral discs.
symptom
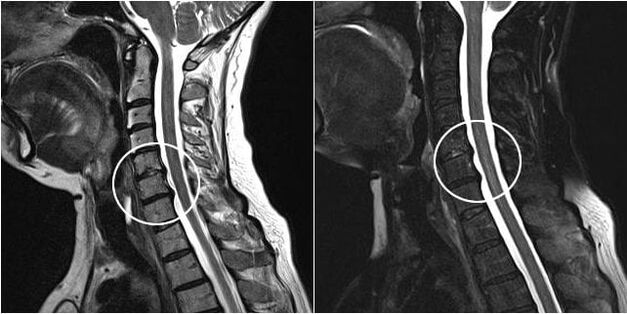
In the first X-ray stage, the signs of osteochondrosis are weak. Only the uneven surface of the disc is noticed. Therefore, women experience only mild neck discomfort after physical exertion or after holding their head down for a long time. But gradually increase the intensity of the pain. It occurs not only when turning and tilting the head, but also when resting. Pathology is progressing steadily without medical intervention. Due to osteophyte invasion, the vertebral artery and intervertebral disc are displaced, resulting in the following clinical manifestations:
- a jump in blood pressure;
- headache (cervical migraine), dizziness, fainting;
- decreased vision and hearing, double vision of objects in front of the eyes, tinnitus;
- fatigue, apathy, sleep disturbance;
- Throat itching, a "coma" feeling.

Also, when tilting or turning the head, a creaking sound is heard and movement in the neck area is restricted.
pathological diagnosis
The initial diagnosis can be made on the basis of external examination, patient complaints, and the results of several functional tests to assess range of motion, reflexes, and sensitivity. To confirm this, radiographs were performed in 2 projections. The study not only helps to detect osteochondrosis, but also to determine its stage, the extent of damage to the discs and vertebrae. Discography can accurately examine the affected disc and, if nerve pathway damage is suspected, can show the patient an electrophysiological diagnosis:
- evoked potential;
- electroneurogram;
- EMG.
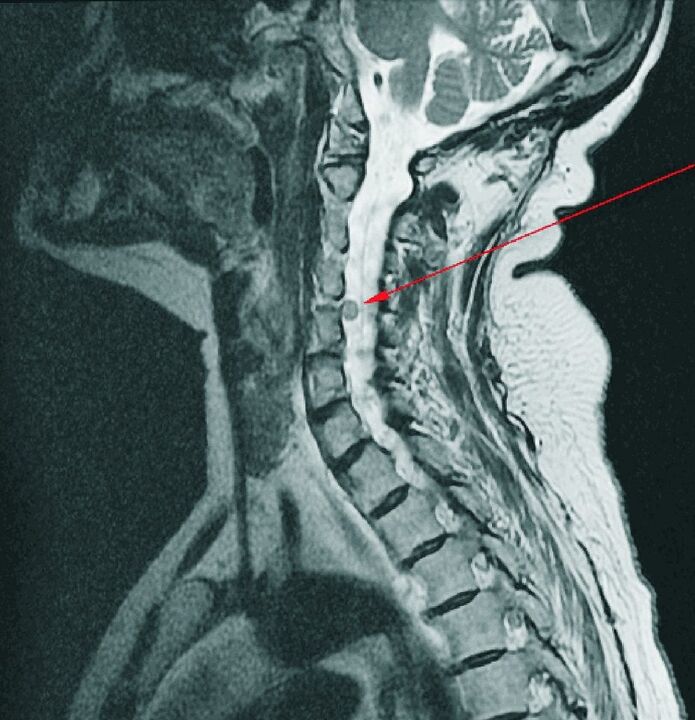
CT, MRI are often used as additional diagnostic methods to assess the condition of the spinal cord, to detect complications - herniation or herniation. These studies were conducted to differentiate cervical osteochondrosis from tuberculous spondylitis, osteomyelitis, benign and malignant tumors, ankylosing spondylitis, and rheumatism.
emergency first aid
During a relapse of cervical osteochondrosis, the neck pain is so severe that women are afraid to turn or tilt their head. To reduce its intensity, lie down on a hard surface. It is necessary to adopt body positions where the pain subsides. If a Shants collar or semi-rigid bandage has been purchased on the advice of a doctor, it must be worn while moving.
Stopping pain attacks will allow taking any non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) tablet. Ointments and gels containing NSAIDs have significant analgesic effects.
When giving first aid, it is not desirable to use cold or heat. Often, with relapses due to muscle spasms, cold compresses only increase skeletal muscle tone. Dry heat is an effective way to relieve symptoms, but only if there is no inflammatory process in the soft tissues of the neck.
How to treat cervical osteochondrosis in women
Osteochondrosis of any localization has not been completely cured. A neurologist or chiropractor will certainly explain to the woman the meaning and principles of the upcoming treatment. Treatment is aimed at achieving stable remission. During this phase, any painful sensations are minimal and the range of motion is fully preserved.

It is not possible to be limited to taking medication, because the means of restoring the discs and vertebrae have not yet been synthesized. It is necessary to follow all the doctor's prescriptions - to participate in physiotherapy, massage activities, sports therapy and gymnastics.
From the first day of treatment, patients are advised to wear a Shants collar - an orthopaedic device that stabilizes the discs and vertebrae. They prevent displacement of vertebral structures, thereby reducing the likelihood of recurrence.
Overview of Therapeutic Drugs
Sometimes during the deterioration of cervical osteochondrosis, there is a burning, tingling pain due to the invasion of the base of the spine. They can only be eliminated by intramuscular injection of an NSAID solution. If they are ineffective, drug blockade with anesthetics and hormonal drugs. Glucocorticoids are used infrequently because of their negative effects on internal organs, cartilage, and bone tissue.
To get rid of mild pain, women can take NSAIDs in tablet or capsule form. Nonsteroidal medications in the form of gels and ointments are used for mild pain, as well as to reduce the dose of systemic medications.
| A set of drugs for the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis | Therapeutic effect |
|---|---|
| chondroprotective agent | Partial restoration of intervertebral disc cartilage tissue |
| Ways to improve blood circulation | Eliminates oxygen and nutrient deficiencies and promotes regeneration |
| B vitamins | Normalizes impulse transmission to the central and peripheral nervous system |
| muscle relaxant | Relax skeletal muscles and eliminate muscle spasms |
| warm ointment | Accelerates blood circulation, has analgesic and anti-exudation effects |
| Antidepressants, tranquilizers, tranquilizers | Alleviate increased anxiety, restlessness, sleep disturbance |
therapeutic exercise, gymnastics, exercise
The most effective way to treat osteochondrosis is daily exercise therapy. With the help of dose loading on the cervical spine, the muscular corset is strengthened, the blood supply to the tissues is improved, and the risk of deterioration is reduced. It is necessary to start gymnastics as soon as the acute pain stops. An exercise therapist will develop a separate set of exercises for a woman based on her physical health and the severity of the disease. All movements went smoothly, with small amplitudes. This will strengthen the muscles without damaging the cartilage tissue. Which exercises do physical therapists recommend:
- Sit up straight and place your hands under your chin. Try tilting your head and resist with a brush;
- In a seated position, place your hands on your cheeks. Tilt your head to one side and resist with a brush;
- Stand up and put your hands on the belt. Rotate your head in one direction and then in the other without leaning back too much.
Swimming, yoga, Pilates, water aerobics, Nordic walking are recommended for patients with osteochondrosis. Cycling, running, and weight lifting are prohibited.

Nutrition and Diet
For cervical osteochondrosis, nutritionists recommend limiting alcohol, coffee, and strong tea use. These beverages interfere with calcium absorption, rapidly expelling it from the body. Priority should be given to lightly salted mineral water, fruit preserves and jellies, vegetable juices, and berry juice drinks. The optimal water intake is 2-2. 5 liters per day.
Fast food, semi-finished products, bacon, fatty meat must be abandoned. The daily dietary menu should include fresh fruits and vegetables, cereals, dry white or rye bread, and fermented dairy products. Useful for turkey, chicken breast, rabbit, lamb. 2-3 times a week you need to eat some oily fish like salmon or Norwegian herring.
It's best to give up fried foods entirely. The most useful products are baked in foil, simmered in water or steamed.
physiotherapy
During the recovery phase, patients are assigned 5-10 sessions of physical therapy. Electrophoresis or ultrasound electrophoresis with chondroprotective agents, calcium salt solutions, B vitamins to restore cartilage tissue, improve innervation, and increase the strength of ligament-tendon devices. The same procedure, but with glucocorticoids, analgesics, and anesthetics only in the subacute phase, aimed at relieving pain and inflammation.
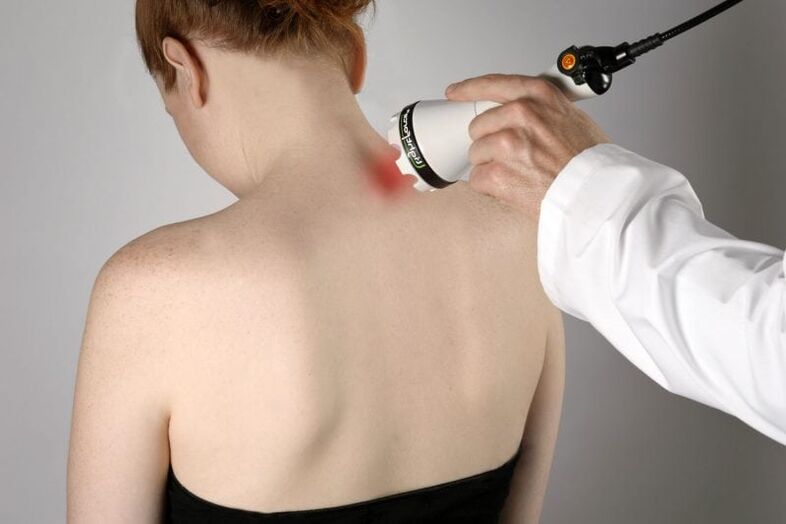
The following physical therapy procedures can also improve women's health:

- Ultra high frequency treatment;
- magnetic therapy;
- current;
- Laser Treatment;
- Shockwave therapy.
Applications using ozokerite, magnesite, paraffin. The use of therapeutic mud and mineral water, the setting of medical leech has proven to be very effective in the treatment of cervical osteochondrosis.
massage
During the massage, the muscles of the entire back are mechanically affected, not just the neck area. But experts pay special attention to them. Thanks to the kneading, smoothing, pressing and chopping actions, spasmodic skeletal muscles relax, ligaments strengthen and blood circulation improves. In the treatment of osteochondrosis, the following types of manual and hardware massage are used:
- classical;
- View;
- vacuum;
- Sweden;
- segmented.
Pharmacies and medical device stores sell hand-operated electric massagers. They are equipped with special nozzles, speed controllers. The comfortable long handle of the device allows you to massage the back of the neck independently.
folk remedies
In folk medicine, homemade ointments, alcohol and oil rubs, compresses, decoctions, and tinctures are used to treat osteochondrosis. Official medical representatives are skeptical of treatments for this degenerative dystrophic pathology due to low clinical effectiveness. Exceptions are herbal teas derived from chamomile, St. John's wort, and rose hip infusions.

Treatment characteristics of elderly women
Treatment of elderly patients is performed using the same techniques as treatment of younger women. But neurologists take into account the presence of chronic disease in older adults, and decreased functional activity of the liver, kidneys, and gastrointestinal tract when determining the dosage regimen. Doctors choose drugs, using drugs that have less impact on internal organs and reduce the risk of adverse effects.
What is Dangerous Cervical Osteochondrosis
The main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis are similar in both sexes. But neurological symptoms were more pronounced in women. They are more often diagnosed with violations of the vertebral roots and vertebral arteries that supply the brain.
In Severity 2 and 3 cervical osteochondrosis, the vertebral base is usually invaded, resulting in acute pain, loss of reflexes, and decreased sensitivity. Serious complications of pathology are intervertebral hernia, radiculopathy, discogenic myelopathy.
Precaution
Cervical osteochondrosis is frequently detected in women who prefer to wear narrow shoes with high heels. When worn, the load on the spine is unevenly distributed, resulting in minimal trauma to the cartilage tissue. Women also frequently suffer from hypothermia, and they are experiencing ordinary family conflict violently. These factors are prerequisites for the development of pathology. Therefore, excluding them from the usual lifestyle becomes an excellent way to prevent osteochondrosis of any localization and its consequences.

























