Osteocartilage degeneration in the lumbar area is a chronic degenerative disease of the lumbar spine, which affects the structure of the intervertebral disc and many lumbar spines located in the lumbar spine.It affects people of major working age.It shows various symptoms, the main one being pain in the lower back and legs, limiting movement in the lower back.For diagnosis, research methods such as lumbar radiography, computed tomography or magnetic resonance tomography were used.In this article, you can provide more detailed descriptions of the causes, symptoms and methods for diagnosing lumbar osteochondrosis.
Osteocartilage degeneration is the result of human aging.These or other signs of these diseases can be found in almost everyone (!) who starts at the age of 25.But this is the severity of these changes, the speed of their progress, the extent to which they are clinically manifested depends on many reasons, mainly on how a healthy lifestyle leads to a particular person.When doing multiple tasks (gardens, buildings, mediocre cleaning of the house, etc.), physical exercise, mandatory morning gymnastics, correct posture of the body, orthopedic mattresses are the moment when the lumbar vertebrae changes.
According to statistics, in 80% of cases, osteochondrosis in the spine is the cause of back pain.
How does osteochondrosis develop?
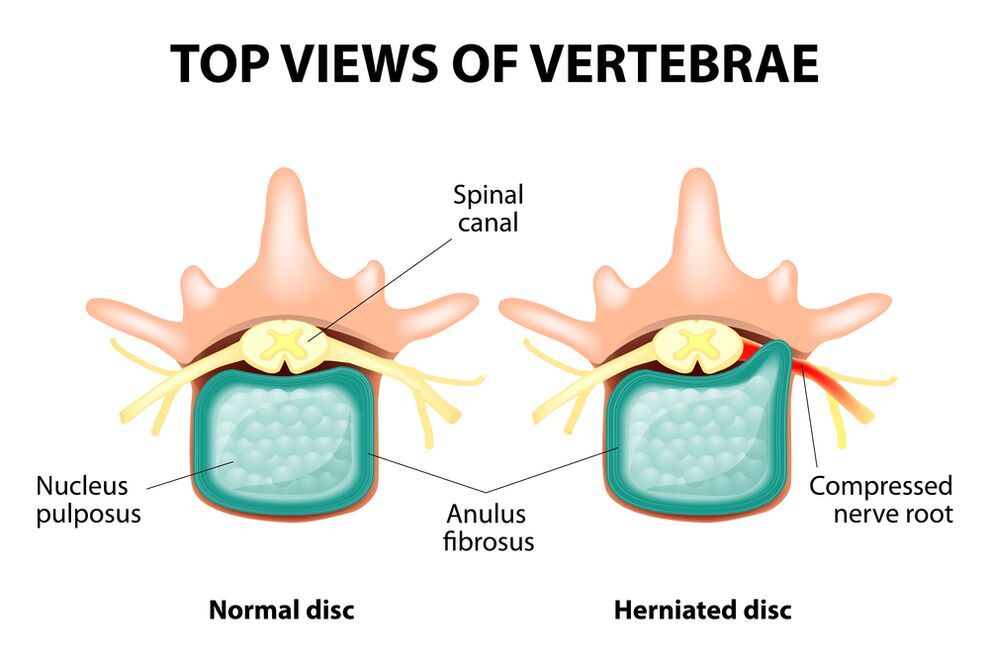
The entire spine is composed of separate vertebrae, and intervertebral discs exist between their bodies.That is, there is a disk between the two vertebrae.The disk consists of a gel-like (pulp) nucleus and a fibrous annulus.The core contains a lot of water and provides depreciation and flexibility of the spine.The fiber ring is located around the jacket core, as if it is fixed inside itself.
As the load on the dock core extends, it changes its physiological properties, loses water and dryness, and the final sequence: the disk is flattened and the vertebrae are close to each other.With this process, in the outer jacket of the cell nucleus, the fibrous annulus will lose its elasticity and begin to protrude under the influence of mechanical loads.This is called prominent.Then, the annular fibrous fibrous cracks and the gel-like nucleus falls through the resulting gap: a hernia of the intervertebral disc occurs.A map of two adjacent vertebrae and a disc located between them, called vertebrae segments, obtains excess mobility, thereby increasing the load on nearby segments.Overload in adjacent segments triggers a similar pathological process.These changes are called osteochondrosis.
To somehow ensure the stability of the spine, bone growth is formed along the edge of the vertebral body, thereby increasing the support area.This phenomenon is called spondylosis.The changes in the joint between the vertebrae are called spondyloarthritis.Generally, all three pathologies - osteochondrosis, spondylosis, spondylitis - walk nearby.
reason
Why does osteochondrosis occur?So far, there are several theories that have occurred:
- Mechanical Theory: Perhaps it should be believed that the main reason is the normal increase in load on the spine.That's why osteochondrosis is almost the fate of moving workers, miners, builders and people.The occurrence of osteochondrosis in the waist area is mainly related to the degree of lifting of slopes and weightlifting, which forces the working position to be uncomfortable.
- Another factor in development is incorrect posture, sitting in the wrong posture, which is particularly relevant to the mental worker.
- Sometimes, roles are played by the genetic characteristics of the spinal structure and the nutrition of the individual structures.
- Trauma theory: Any trauma in the spine, even the least tiny, can initiate a degenerate process;
- Hormonal metabolic and endocrine diseases can adversely affect the metabolism of spinal tissue and contribute to the development of osteochondrosis.
- Age theory means natural wear of the intervertebral discs during life.
In each case, few of these theories can explain the occurrence of osteochondrosis.At the same time, there are more factors of "blame".
In the event of lumbar osteocartilage degeneration, overweight plays an important role because it itself is an overload of the spine.The higher the body mass index (obesity level), the more obvious the spine changes.Among other reasons, the occurrence of osteochondrosis can also be noted:
- A sedentary lifestyle;
- Imorly nutrition (fast food, excess sweetness, semi-produced products: all of which lead to imbalances of trace elements), and lack of liquids;
- abnormalities in spinal structure (e.g., the presence of additional lumbar spine);
- shoes that are constantly wearing high shoes;
- Pregnancy (due to excessive burden on the lumbar spine);
- Abruptly terminate training for those who participate in sports professionally;
- Smoking and alcohol abuse: as a factor that accelerates the aging process in the body.
symptom
The main manifestation of lumbar osteochondrosis is pain.The nature of the pain, where it occurs and the direction of distribution depends on the stimulation of the receptor, that is, the rough changes in the intervertebral disc and surrounding tissue, the appearance of herniation or hernia, in which directions are protrusions, etc.
Reflex and compression syndrome are distinguished by lumbar osteochondrosis.
Reflex syndrome occurs when the annular fibrous receptors of nearby affected discs, ligaments and joint capsules are stimulated.They are reflexive because in addition to pain, they are accompanied by changes in muscle tone, nutrition-vascular or neuronal reflexes, that is, the stimulation of the reflex also spreads to other structures, mainly from symptoms on the soft tissue side.
Compression syndrome is the result of compression (compression) of nerve roots, blood vessels, or spinal cord formed by changes in osteocartilage.

Lumbar reflex syndrome
Low back pain(feeling): Acute sudden pain in the lower back occurs when there is awkward movement or body tension (much less for obvious reasons).It is believed that the occurrence of cashew nuts is related to the movement of the jacket core within the fibrous annulus, that is, it develops in the initial stages of osteocartilage.Often, pain is described as “feeling” and “the stake is trapped in the lower back.”The patient freezes in a pain-captured position.The slightest movement can cause increased pain (sneezing, coughing, trying to lie on the bed, moving your feet).If a person is in a tilted position when developing (this happens most often), then he cannot understand.A noticeable muscle voltage reflex in the lumbar spine appears.Along the vertebrae in this area, muscle rollers are felt, and sometimes the muscles cannot be seen with the naked eye, and the muscle tension is so obvious.Feeling pain for the patient.This increased muscle tone plays a fixation role, protecting the affected waist fragment from pathological mobility, which may lead to worsening in the state.The natural curvature of the lower back spine is flattened, perhaps due to muscle tension, which may be curvature (scoliosis).
Low back pain- Another reflex syndrome at the waist level.The term also means pain in the waist area.However, unlike cashew nuts, the pain does not appear sharply, but gradually occurs within hours or even days.The pain is stupid, moderately intense and can be exacerbated during movement when sitting or standing positions move from one position to another.A little relief makes the back position of lying down or the lower back of the back, but the passive elevation of the straightened legs in that position can cause increased pain in the lower back (LASSA symptoms).The palpation of the lumbar spine is painful, but the reflex tension of the muscles is not as strong as that of the cashew nuts, and sometimes there is no such thing as it is.The movement of the lumbar spine is limited, but it is possible.This means that the patient can bend downward and sideways to a certain level (and then the pain becomes worse).
Sciatica- Another reflex syndrome at the waist level.To this term refers to pain in the lower back, the back will give to the hips and legs (on the back surface).Pain is different, mostly pain, but can be aggravated regularly by the type of "fireplace" on the legs.Just like Lumbalgia, it strengthens with any movement, walking, nervousness, lying on the back.Symptoms of LASSA are usually positive.The palpation of the lumbar spine is painful and pressed at certain points (e.g., the middle of the line, separate the hips from the thighs, the middle of the back of the thighs, the middle of the popliteal Fossa).The lower back muscles are tense.The tilt forward and side sides is limited.

Lumbar compression syndrome
Clinical characteristics depend on which structure is compressed.
Between the vertebrae in each foramen are the nerve roots (spinal nerves): left and right.If the pathological formation of lumbar osteocartilage degeneration (mainly the disc of the intervertebral disc) squeezes the root, it will develop, and radiculopathy will occur, and the symptoms of each root are different.Commonly common to all radiation diseases in the waist area are sneezing, coughing, lower back movement (especially forward tilting), muscle tension in the lower back, and limitations of lumbar movement.The following types of lumbar spine are the most common:
- radiculopathy L1, L2, L3: Pain occurs in the lower back, giving the expected thigh.In the same area, the occurrence of sensory abnormalities (a crawling chicken skin, numbness) is possible, and superficial sensitivity is disturbed (no distinction from the usual acute touch, cold and hot sensations) disappear.The knee reflex is reduced, and the weaknesses of the quadriceps in the thigh are revealed.
- Root disease L4: Pain in the lower back gives the front line of the thigh, the inner surface of the knee joint, and slightly lower along the inner surface of the lower leg.In the same area, abnormalities are felt and surface sensitivity disappears (reduces).The weakness of the quadriceps muscles in the thigh will also develop, and the knee reflexes will be reduced.
- radiculopathy L5: One of the frequent positioning.The pain follows the outer edge of the thigh, and the front surface of the lower leg follows the inner edge of the foot to the inner edge of the foot.Anomalies are felt here, surface sensitivity is disturbed, and pain can be felt when sneezing and coughing.Also, since the muscles of the foot are difficult to stretch, the Kine L5 governs the muscles that perform this action.Sometimes it is difficult to stand on the heel with your bare feet.
- S1 radiation disease is often found in lumbar vertebrae.The pain follows the outer edge of the thigh, the outer edge of the lower leg to the outer edge of the foot to the outer edge of the foot and the heel of the fifth finger.These areas are characterized by abnormal sensation and reduced surface sensitivity.Achilles reflexes decrease.As a result of damage to the spine, weaknesses in the muscles of the lower leg and foot flexor muscles develop, making it difficult to stand on the socks and walk.
Several root radiation diseases can be developed simultaneously, especially the characteristics of L5 and S1.It happened that a hernia squeezed several pieces.
If the disc community is behind, it can squeeze the spinal cord.This is only possible if the hernia is located in the upper reference point, as there is no spinal cord vertebra below the lumbar vertebra (the root of the spinal cord is compressed and the caudal equine syndrome will form).
If blood vessels in the lumbar area are squeezed by squeezes, which flow blood to the spinal cord, a spinal stroke can develop and compress for a long time in the event of acute circulatory disease - bone marrow disease.Bone marrow disease is a bilateral weakness of the leg muscles, which starts from the feet and gradually develops.The sensitivity of the legs is disturbed, the Achilles reflex is lost, and the knee is lost.There is a possibility of urination disorders (there are often "imperative" urges that require immediate satisfaction and urinary incontinence).
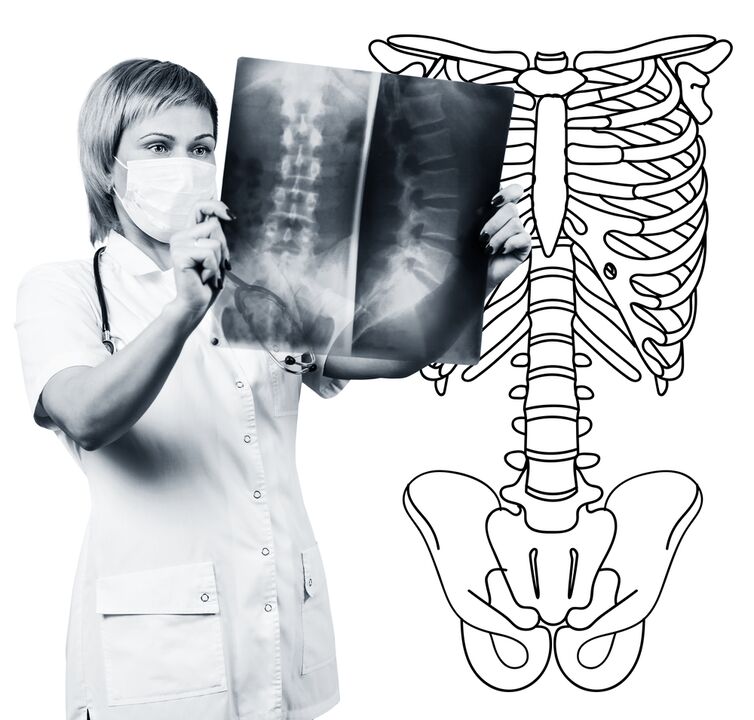
Diagnostic method
The diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis is based on clinical data and data from other research methods.Key roles belong to this method:
- Radiography of the lumbar spine;
- Computed lumbar tomography;
- Magnetic resonance tomography of the lumbar spine.
X-rays of the lumbar spine must be performed in 2 projections that are perpendicular to each other - straight tail and side.Images like this allow you to see the shape, profile and structure of the vertebrae, the height and shape of the disc, abnormal spine, and natural curves.To show the vertebral joint and intervertebral foramen, a radiography is generated in the sloping projection.To identify pathological mobility of individual lumbar fragments (which is a sign of osteochondrosis), X-ray photography was performed under the conditions of functional tests, i.e., spinal flexion and expansion.Generally, you can clearly see that the height of the disc changes depending on the direction of the body's inclination, and the height of the disc does not change when it is bent or stretched due to the osteocartilage changes caused by the functional blocks of one of the fragments.By pathological mobility, the forward or posterior displacement of the vertebrae was determined.The main X-ray signs of osteochondrosis include stenosis of the vertebral slit, pathological mobility and displacement of the vertebral body, deposition of salt in intervertebral disc tissue (calcification), regional growth of the vertebral body, regional growth of the vertebral body, compaction of the vertebral body, bordering (on the vertebral bone) in contact with the intimate disk (appropriate bone).Radiography of the lumbar spine is a routine study that gradually loses its significance in the context of proactively implementing new and more informative research methods (CT and MRI).Today, radiographs in the waist department are used as screening diagnostic methods.
CT of the lumbar spine is also performed using X-ray radiation, but the radial load in the body is much smaller than that in X-rays.The study was performed on a table with special equipment - a computed tomography, absolutely no pain.Use computers to process the resulting pictures and let you see more structures than spinal X-rays.
MRI is a method of using electromagnetic radiation to create images.The study was also conducted in a position lying on a table summoned to the scattering room.MRI is harmless and painless.
A CT or MRI of the lumbar spine allows you to see all the structure of the spine, carefully examining the disc (as well as the jacket and annulus) and the foramen, the contents of the spinal canal.Even a slight herniation of the intervertebral disc will not be ignored.These methods (especially MRI) allow you to determine the direction of the disc hernia, if any, the degree of compression of the nerve roots, the spinal cord.Therefore, these research methods provide more information than radiographs in diagnosing osteochondrosis in the lumbar spine.Furthermore, they can diagnose not only osteochondrosis but also other diseases (tumours, circulatory diseases in the spinal cord, abscesses, congenital defects in the spinal structure and spinal cord structure), which is important in the differential diagnosis of causes of back pain.
Osteocartilage degeneration in the lumbar spine is a disease that usually causes back pain.In fact, this is the destruction of the intervertebral disc.Due to osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, a person often loses the ability to work because in addition to pain, the disease can also lead to violation of the spine's mobility and inability to sit, stand and walk.The symptoms of the disease are nonspecific and other research methods are needed to accurately confirm the diagnosis.Modern osteochondrosis diagnosis methods are the most useful and safest method is MRI of the spine.

























