Hip arthritis (coronary heart disease)- This is a chronic degenerative joint disease that causes deformation of bone tissue.Together with Coksartrosis, all components of the joint are involved in the pathological process: articular cartilage, bone structure adjacent to the cartilage, synovial shell, ligaments, capsules, and adjacent muscles.If a disease occurs, the articular cartilage is destroyed, the micromass of the bone and bone plants appear (bone growth), and inflammation of the hip muscle ligament occurs.
In the world, every fifth person complains about joint joint problems.This can be pain or limitation of movement in the joints, and a combination of these symptoms.Vision in the clinic falls on patients with bone and muscle disease every second, while 66% of cases are those under the age of 65.According to the latest epidemiological research, the prevalence of knee and hip joints in the adult population is 13%.
Risk factors for developing coronary heart disease:
- Genetic tendency.A common cause of coksarrosis in hip joints is mutations in congenital or acquired type II Prollagen type.
- Old age.The possible reason for the prevalence of arthritis in the elderly is the destructive effect on the external environment of articular cartilage and its resilience.
- ground.Women suffer from osteoarthritis more frequently than men.This is due to the effect of estrogen female sex hormones on bone mineral metabolism.However, the effects of flooring are ambiguous – according to some authors, unlike other joint damage, the sexual basis of sexuality is not different: in men, arthritis of the hip joint is as often found as women.
- Too much weight.This relationship is demonstrated between overweight and the occurrence of arthritis.Excess bonding tissue increases damage load on the cartilage.In addition, adipose tissue produces proinflammatory enzymes that damage cartilage tissue.
- Frequently develop bones and joints.According to the study, 80% of coxhrosis that occurs without obvious causes is associated with defects in previously undiagnosed hip dysplasia and subluxation.
- Heavy physical labor.Excessive load on the hip with certain types of manual labor can lead to joint damage and joint formation.At risk are agricultural workers, diggers and people with similar professional work.
- Injuried.The risk of competitive development increases after a hip injury.Additionally, an injured joint and both can participate in this process.
- Professional sports.Due to excessive joint burden and injury, professional sports can cause cruisers to occur.Potentially dangerous sports include heavy track and field, track and field, parachute.
- Bone and joint diseases- Rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, joint infection, vascular necrosis, gout arthritis, etc.
- Endocrine pathology- Hypothyroidism, hypothyroidism, acromegaly (impaired pituitary anterior function), diabetes, obesity.
If similar symptoms are detected, consult your doctor.Don't intervene yourself - it's dangerous to your health!
Symptoms of hip arthritis
The main symptoms of fifty-ball arthritis include: joint pain, mobility limitation and tightening, their deformation, shortening of the function of the lower limbs, and periodic swelling of the joints.
Pain of all magnitudes.The pain in the joints is initially insignificant and occurs in a short period of time.They appear or intensify when walking or other physical fatigue, such as squatting, tilting, and lifting weights.As the disease progresses, the pain will increase and even a long period of rest will not be relieved.In addition, pain occurs for a long time and joint fixation in one position.
Patients complain about SO pain in hip joints after sleeping, driving a car and other prolonged fixation.Coxarlthis' "start" pain lasts no more than 30 minutes.Pain can increase during hypothermia or under stress.They can be positioned on the area of the hip or groin, on the front surface or side of the thigh.As the pain spreads over the nerves of the lumbar nerve, it can be spread to the thighs away from the center of the body or the knee.Sometimes, pain applies to the lumbar spine and coccyx.
Limitations of joint movement.Due to the pain, the movement of the hip joints in the hip joint is limited.Meanwhile, rotation (inner and outwardly) and the lower limbs (moving to the middle of the body) are more disturbed, but may be limited (moving from the central axis of the body), as well as buckling and extension.Due to obvious pain syndrome, being unable to perform passive movements in the joints can lead to pelvic bias.The patient's gait changed, with the hip protruding backwards and the body deviating forward as the weight shifts to the damaged side.A "duck gait" was formed under bilateral damage in patients with Coksartrosis.
With the periodicity of patrolSwelling of the jointsThis is invisible due to the muscle and fat layer.Moreover, the disease is characteristicThe crystals in the joints during movement, the gradual deformation and shortening of the lower limbs.
Usually, one joint is affected by a disease, and the process then applies to other diseases.But sometimes arthritis affects several joints at a time and multisomal arthritis occurs.Multisomal arthritis is a characteristic of older people or hereditary tendencies and concomitant diseases - a disease of bone, joint and endocrine diseases.
Pathogenesis of hip arthritis
In the pathogenesis of hip arthritis, mechanical damage (caused by increased body application on the joint) and genetic, hormones and metabolic factors play an important role.It is often impossible to find out which factors affect the development of the disease in a particular patient, but this disease usually develops after tissue damage due to mechanical damage.
Damage to tissue stimulates the division of cartilage tissue cells (chondrocytes), while the production of proinflammatory cytokines increases, usually only in small amounts of cartilage.Cytokines trigger inflammatory processes, for example, under the influence of the proinflammatory cytokine IL-1, the enzyme is the enzyme that distinguishes the damage to articular cartilage.Similarly, under the influence of cytokines, the production of TSOG-2 enzymes and other substances that have toxic effects on cartilage is also increased.
Synovial membranes also play an important role in inflammatory diseases of the synovial shell of rotating joint shells or ligaments, as liquids accumulate in the cavity.
The reduction in elasticity and strength of articular cartilage associated with metabolic diseases can lead to its resistance to mechanical stress.Using Coksartrosis, all components of the joint are involved in the pathological process, including subchondral bone.Because the large joints of the lower limbs are caused by the large joints of the human body, they encounter obvious mechanical stresses, which are due to microshell tumors occurring in the microshell plates and the lower part of the cartilage.As a result of microorganisms, the subchondral bone is compressed, resulting in the growth of bone tissue-area bone plant.This in turn stimulates further degradation of articular cartilage.
In some cases, joint inheritance of the hip joint is inherited.Hereditary arthritis is said to be the inheritance of multiple genes - each has a weak effect due to the role of many genes.Some diseases are caused by mutations in genes encoding articular cartilage macromolecules, which can cause them to rupture.The genes responsible for chondrocyte division may also be affected.Furthermore, metabolic diseases are inherited, such as pyroarthritis - a disease in which calcium pyrophosphate crystals accumulate in articular cartilage and synovial fluid.
Classification and development stages of hip arthritis
Depending on the cause of the disease, Fifty Balls are dedicated to two main forms: primary (idiopathic) and secondary (caused by other diseases).
Primary Coksartrosis:
- Local (only hip effects):
- unilateral;
- bilateral.
- To summarize (poly bowel cancer), at least three joint groups of lesions (e.g. hips, knees, and small joints of the brush or feet).
Sub-joint joints:
- Posts - Trauma:
- Acute - Due to acute injury;
- Chronic - The result of certain exercise courses or professional activities.
- Metabolic diseases (respiratory disorders, hemochromatin tumor disease, Wilson's disease, Goche's disease).
- Congenital pathology and developmental defects (congenital dysplasia of the hip, pertes disease, epiphyse slip of the femur, hypermotor syndrome, lower limb shortening, scoliosis, skeletal insufficiency).
- Endocrine pathology (acute hypertrophy, hypothyroidism, diabetes, hyperthyroidism, obesity).
- Calcium salts (pyroarthritis, calcified tendonitis).
- Diseases of bones and joints (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, childhood diseases, vascular necrosis, infection).
According to clinical manifestations, the following forms of coronary heart disease are distinguished:
- Almost no symptoms.
- Showing bright clinical symptoms:
- Progress quickly, symptoms appear in the first four years after the onset of the disease;
- Five years after the disease, symptoms of slow progression were shown.
Two types of hip arthritis can be identified based on X-ray pictures:
- Hypertrophicity - with signs of increased repair response (e.g., the appearance of ossification agents of the bone, replacing the lesion with new tissue);
- atrophy (decreased tissue volume).
The stage of the disease can be determined radiologically and clinically.To determine the radiological stage of hip joint articular joints, the classification of Kellgren and Lawrence (1957) is most commonly used.
The stage of arthritis in radiological classification
| stage | Logo |
|---|---|
| 0 | No signs of joints in X-ray images |
| 1 | Joint gap has not changed, single area bone plant visualization |
| 2 | The joint gap has not changed, visualizing obvious regional bone plants |
| 3 | The height of joint space is moderately reduced, visualizing obvious regional bone plants |
| 4 | The height of joint space is significantly reduced, with significant regional bone plant and subchondral bone sclerosis visualized (under the cartilage structure, compaction of bone tissue under the subchondral surface) |
To determine the clinical stage of the disease, classification (1961), which uses clinical signs and visualization criteria.
The clinical stage of joints
| stage | Logo |
|---|---|
| 0 | The joint space is clearly and unevenly narrow, the edges of the joint cracks are slightly sharp (initial bone plant), with a slight limitation on movement |
| 1 | The joint space was significantly narrowed (50-60%), with obvious cystic heuristics in osteogens, subchondral bone sclerosis and cystic heuristics in osteophysees.The clinic is limited mainly by mobility in joints, rough tightness during exercise, insignificant or moderate muscle atrophy |
| 2 | Deformation, joint stiffness; joint space is reduced by more than 60-70% normative or completely absent, extensive bone plants, subchondral cysts, joint "mouse" |
Complications of hip arthritis
With the influence of duality, all complications are fully correlated with pathological changes in the joints.
Local inflammatory processes can complicate the process of Coksartrosis:
- BURSITE-Inflammation of bursals in joints;
- Tendonitis - Inflammation of the inner shell of the muscle tendon vagina;
- Tunnel syndrome forceps that cause nerves due to the formation of large bone genus or joint deformation.
With competitive progress and its transition to the clinical stages of II and III, pain limits the mobility of the joints and over time, joint stitches (fibers, bones, or cartilage) occur with its complete fixation.
Significant joint deformation can causeFracture or sterile necrosis of the bone.For Coksartrosos, sterile necrosis of the femoral head is the most powerful complication.
There is obvious coksartrosis that may occurSubluxation and dislocation of jointsand the femoral head penetrates into the pelvic cavity.Dislocations and subluxation of the hip joint can cause pain (acute at first, then dull and sore), aggravated during walking and other physical fatigue, as well as deformation of the joints, lax feet, and sometimes shortening the affected limbs.
Despite the lack of systematic manifestations of arthritis itself, more attention has been paid to the diseases associated with it in modern clinical practice.These are such pathological conditions that exist or occur in the context of the current disease.Related to inflammatory responses caused during joint processes, the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the inner wall of blood vessels is enhanced, thereby increasing the riskCardiovascular disease.Due to limitations in pain and joint mobility, the reduction in physical exercise results inObesity, depression and worsening quality of life.Long-term use of non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs,The upper gastrointestinal tract is affected,besidesIncreased risk of cardiovascular pathology and renal disease.
Diagnosis of hip arthritis
The diagnosis of "Coksartrosis" was diagnosed based on clinical manifestations and radiological examinations.There are no signature laboratory signs used to diagnose joints.
In clinical manifestationsThe main diagnosis of hip joints is pain and its characteristics.Pain in the hip joint joint occurs and gradually grows over a few years (sometimes in a rapid progression form for several months).Pain occurs or increases when the body is exhausted or in a standing position.If the patient starts to feel pain alone, inflammation (synovitis) is added.Statement is up to 30 minutes in the morning and fixed for a long time.
Limitations of joint mobility are gradually increasing, which applies to active and passive movements.As the disease progresses, joints deform, and the function of limb length may be shortened.
Perform a physical inspectionJoint mobility, its deformation, shortening of limbs, pain in joint palpation, and a large rotation of femoral muscle atrophy are limited.
Laboratory methodsTo diagnose arthritis in the hip joint.However, they can be used to diagnose the diagnoses of arthritis (rheumatoid and chronic) because there is no inflammatory change in arthritis and no increase in uric acid levels.In addition, using laboratory tests revealed contraindications for drug treatment methods.
Musical instrument methodTo diagnose arthritis in hip joints:
- Radiography- This is the main method for diagnosing hip arthritis.X-rays identified the changes in Coksartrosis: stenosis in the joint space, changes in bone plants, cartilage, subchondral cysts and bone sclerosis.X-ray is a classic method to diagnose duality, and radiological signs are the basis of competitive classification.However, at present, joint visualization methods such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging are increasingly used.
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) -The advantage of ultrasound is that there is no radial load in the body.
- Magnetic Resonance Tomography (MRI)- It allows you to see joint damage more clearly than other methods.
- Arthroscopy-Allows you to identify damage to articular cartilage: from the area of cartilage (softening of articular cartilage), diameters less than 10 mm in diameter to deep cracks, to deep cracks, penetrating into the formation of subchondral bones and deep ulcers.shallow and medium cracks and surface erosion can also be seen.
The identification of COKSARTROSIS does not usually represent a particular difficulty, but it is necessary to remember the secondary origin of the hip joints (e.g. complications of other diseases, such as endocrine diseases) when evaluating a specific clinical situation.
Treat the joints of the hip joints
Treatment of hip arthritis can be conservative (drug and non-contractual) or manipulated.Conservative treatment is used in stages 1-2 of the disease for 3 stages.Surgical treatment can be performed in 2 stages and persistent pain and lack response to conservative treatment.
The goal of conservative treatment:
- Improve quality of life - reduce pain and increase joint mobility;
- Stop or slow down the development of the disease.
Non-pharmaceutical treatment methods include:
- Unload the hip joint (weight loss, additional support, and transfer of part of the weight to a crutch or crutch);
- Physical Therapy Sports;
- Physical therapy methods.
Treatment of guri neuropathy begins with non-pharmacological methods and plays an important role in physical therapy practice.Patients should use support due to severe pain.Due to the obvious disease and contraindications of internal worms, support must be used.
Nostril medicationIncludes medications to reduce symptoms of the disease.These are painkillers, as well as those from the non-replacement anti-inflammatory drug (NSAIDS) group.NSAID is divided into non-election and selective.
Analgesics and NSAIDs for pain relief and inflammation are used for joints in hip joints.Currently, there is no evidence of the advantage of one non-replacement anti-inflammatory drug over another, so the choice of a particular drug depends on the side effects and the specific clinical condition caused by it.
It must be remembered that NSAID has many side effects.When taken, they may affect the mucosa of the stomach and duodenum, and as a result may lead to ulcers and bleeding.Many NSAIDs have toxic effects on the liver and kidneys.In addition, NSAIDS destroys platelet aggregation, so the patient is damaged by thrombosis and there is a tendency to bleeding.Prolonged use of NSAID inhibits the hematopoiesis process and may cause sexual anemia and cytosis.The acceptance of selective NSAIDs can lead to a significant reduction in complications.
Locally used ointments and gels have fewer local side effects than oral products.To treat arthritis, warming and pain-relieving medications are used.They can contain turpentine, menthol, niacin, salicylate, bee venom.In addition, NSAID has good results.
In the absence of the effects of analgesics and NSAID, or if the optimal dose of the drug cannot be selected, a centrally-acting painkiller can be prescribed in the short term.
In the case of inflammation, intra-articular administration of corticosteroids is used.Corticosteroids do not exceed 2-3 times a year, as more frequent use can lead to cartilage degeneration.
Slow-acting drugs weaken the symptoms of the disease include cartilage protectors, avocado or soy, inappropriate compounds of hyaluronic acid.These drugs are included in the recommendations of the European Anti-Female Alliance for Anti-Hip Joint Treatment.Prepare to relieve pain and improve joint mobility.
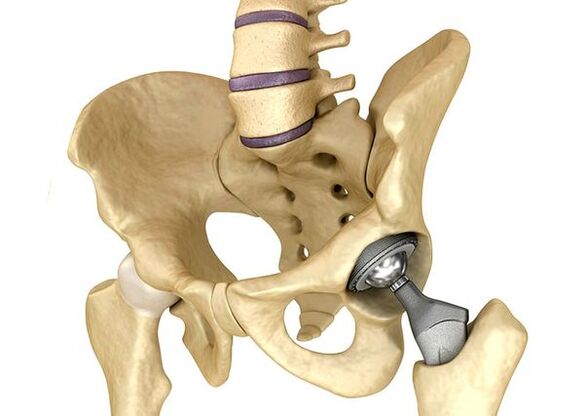
Hip inner tubeIt is used in severe stage 3 when pain syndrome cannot be eliminated and joint mobility is significantly limited.Prosthetics of the hip joint lead to a reduction in pain syndrome, improvement in joint functional status, and the quality of life of the patient.The effect lasts 10-15 years and may require a second operation after that.During the surgery, the hip joint is replaced by artificially mimicking ceramics, metals (typical titanium prosthesis commonly used) or polymers.
forecast.prevention
The prognosis of hip joints is related to the patient's life, but this disease usually leads to disability.According to the World Health Organization, 80% of older patients in the fifty century violated mobility, while 25% were unable to do things every day.In this regard, the main prevention of hip joints is important.
Preventive measures:

- Weight loss.To reduce the weight and load of the joints, it is necessary to adjust the nutrition.Additionally, a decrease in volume of adipose tissue reduces the amount of inflammatory mediators it releases.
- Avoid physical labor and exercise overload.Physical overload is often the cause of hip arthritis, whereas moderate physical activity improves the condition of joint cartilage, retains its normal mobility and reduces load on other joints.
- Correct potential diseases.If the patient is found in a disease that may cause secondary Coksartrosis (endocrine, rheumatism and other patients), the underlying disease must be used.Normalization of hormonal backgrounds and the realization of sustained remission of rheumatoid diseases are both the primary prevention of arthritis and allow you to slow down its development.
- Live a healthy lifestyle.A balanced diet with adequate plant and animal protein, polyunsaturated fatty acids and restricted simple carbohydrates, and moderate physical activity will avoid the occurrence of bovine worms even in the presence of risk factors.
At present, prevention of hip diseases is necessary in neonatology and pediatrics.Over time, adjusted hip congenital dysplasia significantly reduces the risk of CO2 in adulthood.

























